Ubiquitinylation kit![]()
泛素化试剂盒
◆用于合成泛素-E2硫酯的多功能工具
● 能合成一系列由硫酯连接的泛素缀合酶E2的理想方法
● 生物素化的泛素能对连接了链霉亲和素的酶进行灵敏检测
● 试剂盒供50次50 μL的反应使用
泛素化试剂盒是一套在泛素化实验中用于合成泛素-E2硫酯的试剂。该试剂盒利用泛素级联反应中前两个步骤来产生一系列由硫酯连接的泛素缀合酶(E2s);用于将泛素转移至E3泛素连接酶;然后对靶蛋白进行泛素化。生物素化的泛素能有助硫酯的形成,并能对泛素缀合物进行高灵敏度检测。
建议用法
1. 合成用于泛素化实验的泛素-E2硫酯;
2. 在专用的E3泛素连接酶的参与下对靶蛋白进行泛素化;
3. 对用于与新型E2酶通过硫酯连接的泛素进行活化;
4. 使用细胞裂解液或粗提物/制备剂为来源的E3泛素连接酶来促进泛素化;
5. 不依赖底物(目标蛋白)的体外泛素化反应。
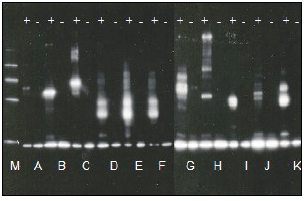
图1. | 酯测试Western Blotting能够适用于所有E2缀合酶。操作步骤按照“Assay Protocol”部分所述的进行。 生物素化-泛素-酶共聚物通过蛋白质印迹法的硫酯测试来检测,其中分别包括: A:UbcH1(Prod. No. BML-UW9020) B:UbcH2(Prod. No. BML-UW9025) C:UbcH3(Prod. No. BML-UW8730) D:UbcH5a(Prod. No. BML-UW9050) E:UbcH5b(Prod. No. BML-UW9060) F:UbcH5c(Prod. No. BML-UW9070) G:UbcH6(Prod. No. BML-UW8710) H:UbcH7(Prod. No. BML-UW9080) I:UbcH8(Prod. No. BML-UW9135) J:UbcH10(Prod. No. BML-UW0960) K:Ubc13/MMS2(Prod. No. BML-UW9565) 而使用“Analysis by Western Blotting”部分所述的链霉亲和素-辣根过氧化物酶检测系统的有M: 生物素化SDS分子量标记(Sigma, SDS-6B) 从下到上:20.1, 29.0, 39.8, 58.1 kDa。 |
◆产品规格
应用注释 | 用法: 1. 在专用的E3泛素连接酶参与下对靶蛋白进行泛素化。E2的家族能够产生E2-Ub硫酯缀合物以用于测试,以 1. 及与特定E3/靶蛋白的结合。例如:p53在mdm2(E3)和UbcH5b(E2)10的参与下进行泛素化。 2. 活化用于将硫酯与新型E2酶缀合的泛素。(在直接可比的条件下,可使用试剂盒中 的E2s作为替代) 3. 使用细胞裂解液或粗提物/制备液作为E3泛素连接酶的来源,在泛素化试剂盒组分的参与下,促进已纯化的 1. 靶蛋白的泛素化。 4. 不依赖底物(目标蛋白)的体外泛素化反应。确定E3酶的泛素连接活性/特异性以及它们的催化结构域/片段 1. 11。 注:应用1和2提供的方案可以通过包含、省略或替代特定的酶组分来修改,从而应用于其他实验。 |
质量 | 试剂盒包含了足够进行4次含有E2酶反应的材料。 |
使用/稳定性 | 试剂盒的所有组分应在-80°C下储存以确保稳定性和活性。 |
储存 | 避免反复冻融 |
运输 | 干冰运输 |
长期储存 | -80℃ |
组分 | 20×泛素活化酶溶液 人,重组 E1(His6-tagged),125 µL,产品编号BML-UW9410 10× 泛素缀合酶溶液 (E2) 每种E2酶有20 µL UbcH1(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9020 UbcH2(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9025 UbcH3(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW8730 UbcH5a(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9050 UbcH5b(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9060 UbcH5c(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9070 UbcH6(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW8710 UbcH7(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9080 UbcH8(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9135 UbcH10(untagged),产品编号:BML-UW0960 UbcH13/Mms2(His6-tagged),产品编号:BML-UW9565 20×生物素化泛素溶液 (Bt-Ub), 125 µL,产品编号:BML-UW8705 20× Mg-ATP溶液,125 µL,产品编号:BML-EW9805 2×非还原性凝胶上样缓冲液,2.5 mL,产品编号:BML-KW9880 10× 泛素化缓冲液,250 µL,产品编号:BML-KW9885 |
产品编号 | 产品名称 | 产品规格 |
Ubiquitinylation kit | 1 kit |
◆相关产品
产品编号 | 产品名称 | 产品规格 |
UBI-QAPTURE-Q kit | 20 tests | |
Ubiquitin conjugating kit (HeLa lysate-based) | 20 tests | |
Auto-ubiquitinylation kit | 10 tests | |
NEDDylation Kit | 20 tests | |
Ubiquitin activating kit | 96 wells |
※ 本页面产品仅供研究用,研究以外不可使用。
参考文献
◆ 产品相关文献
1. | BTK blocks the inhibitory effects of MDM2 on p53 activity: M. Rada, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 106639 (2017), Abstract; Full Text |
2. | Hepatocyte TRAF3 promotes liver steatosis and systemic insulin resistance through targeting TAK1-dependent signalling: P.X. Wang, et al.; Nat. Commun. 7, 10592 (2016), Application(s): In vitro ubiquitination assays, Abstract; Full Text |
3. | Host cell-catalyzed S-palmitoylation mediates Golgi targeting of the Legionella ubiquitin ligase GobX: Y.H. Lin, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 290, 25766 (2015), Application(s): Western Blot, Abstract; Full Text |
4. | TRIM30α Is a Negative-Feedback Regulator of the Intracellular DNA and DNA Virus-Triggered Response by Targeting STING: Y. Wang, et al.; PLoS Pathog. 11, e1005012 (2015),Application(s): In vitro ubiquitination assay, Abstract; Full Text |
5. | TRIM35 negatively regulates TLR7- and TLR9-mediated type I interferon production by targeting IRF7: Y. Wang, et al.;FEBS Lett. 589, 1322 (2015), Application(s): In vitro ubiquitination assay, Abstract; |
6. | Parkin loss of function contributes to RTP801 elevation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease: J. Romaní-Aumedes, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 5, e1364 (2014), Abstract; |
7. | Rlim, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, influences the stability of Stathmin protein in human osteosarcoma cells: X. Chen, et al.; Cell Signal. 26, 1532 (2014), Abstract; |
8. | Stability of the human pregnane X receptor is regulated by E3 ligase UBR5 and serine/threonine kinase DYRK2: S.S. Ong, et al.; Biochem. J. 459, 193 (2014), Abstract; |
9. | Ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of S-RNase in a solanaceous cross-compatibility reaction: T. Entani, et al.; Plant J. 78, 1014 (2014), Abstract; |
10. | E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF126 promotes cancer cell proliferation by targeting the tumor suppressor p21 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation: X. Zhi, et al.; Cancer Res. 73, 385 (2013), Abstract; |
11. | The E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH8 negatively regulates IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation by targeting the IL1RAP coreceptor for ubiquitination and degradation: R. Chen, et al.; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 14128 (2012), Abstract; Full Text |
12. | TRIM32 protein modulates type I interferon induction and cellular antiviral response by targeting MITA/STING protein for K63-linked ubiquitination: J. Zhang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 287, 28646 (2012), Abstract; |
13. | Cullin 4B protein ubiquitin ligase targets peroxiredoxin III for degradation: X. Li, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 286, 32344 (2011), Abstract; Full Text |
14. | Tripartite motif 8 (TRIM8) modulates TNFα- and IL-1β-triggered NF-κB activation by targeting TAK1 for K63-linked polyubiquitination: Q. Li, et al.; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 19341 (2011), Abstract; Full Text |
15. | 1-Benzyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline binds with tubulin beta, a substrate of parkin, and reduces its polyubiquitination: R. Kohta, et al.; J. Neurochem. 114, 1291 (2010), Abstract; |
16. | Pasteurella multocida Toxin-induced Pim-1 expression disrupts suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS)-1 activity: D. Hildebrand, et al.; Cell. Microbiol. 12, 1732 (2010), Abstract; |
17. | The E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF5 targets virus-induced signaling adaptor for ubiquitination and degradation: B. Zhong, et al.; J. Immunol. 184, 6249 (2010), Abstract; Full Text |
18. | The Fbw7 tumor suppressor targets KLF5 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation and suppresses breast cell proliferation: D. Zhao, et al.; Cancer Res. 70, 4728 (2010), Abstract; Full Text |
19. | REUL is a novel E3 ubiquitin ligase and stimulator of retinoic-acid-inducible gene-I: D. Gao, et al.; PLoS One 4, e5760(2009), Abstract; Full Text |
◆一般参考文献
1. | Regulation of p53 by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UbcH5B/C in vivo: M.K. Saville, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 42169 (42169), Abstract; |
2. | Characterization of the novel E3 ubiquitin ligase encoded in exon 3 of herpes simplex virus-1-infected cell protein 0: R. Hagglund, et al.; PNAS 99, 7889 (2002), Abstract; |
3. | Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination: C.M. Pickart, et al.; Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 503 (2001), Abstract; |
4. | Functions of the MDM2 oncoprotein: D.A. Freedman; Cell Mol. Life. Sci. 55, 96 (1999), Abstract; |
5. | Regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein: M. Oren, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 274, 36031(1999), Abstract; |
6. | The p53 pathway: C. Prives, et al.; J. Pathol. 187, 112 (1999), Abstract; |
7. | The ubiquitin-proteasome system and endocytosis: G.J. Strous, et al.; J. Cell. Sci. 112 , 1417 (1999), Abstract; |
8. | The ubiquitin system: A. Hershko, et al.; Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 425 (1998), Abstract; |
9. | Pathways of ubiquitin conjugation: A.L. Haas, et al.; FASEB J. 11, 1257 (1997), Abstract; |
10. | P53 and mdm-2: interactions between tumor suppressor gene and oncogene products: M. Perry, et al.; Mt. Sinai J. Med. 61, 291 (1994), Abstract; |
11. | The p53 tumor suppressor gene: A.J. Levine, et al.; J. Lab. Clin. Med. 123, 817 (1994), Abstract; |
| 免责声明 |
|
1. 本公司密切关注本网站发布的内容,但不保证发布内容的准确性、完整性、可靠性和最新性等。 2. 本公司不保证使用本网站期间不会出现故障或计算机病毒污染的风险。 3. 无论何种原因,使用本网站时给用户或第三方造成的任何不利或损害,本公司概不负责。此外,对于用户与其他用户或第三方之间因本网站发生的任何交易、通讯 3. 或纠纷,本公司概不负责。 4. 本网站可提供的所有产品和服务均不得用于人体或动物的临床诊断或治疗,仅可用于科研等非医疗目的。如任何用户将本网站提供的产品和服务用于临床诊断或治 4. 疗,以及其他特定的用途或行为,本公司概不保证其安全性和有效性,并且不负任何相关的法律责任。 |