NGAL (human) ELISA kit![]()
肾损伤标志物 NGAL 检测试剂盒
急性肾损伤(Acute Kidney Injury,AKI)是一组临床综合征,以急性肾功能(Acute Renal Failure,ARF)减退为特征。针对 AKI 的诊断及研究,已证实存在于血液或尿液中的多种蛋白可成为肾损伤、肾疾病或肾毒性诊断及愈后的标志物。
其中,中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白(NGAL,lipocalin-2,siderocalin)是一种 25 kDa 的小蛋白,在全身上皮组织中表达。其可作为肾损伤标志物,当肾小管损伤后,NGAL 可从患者的尿液和血液中检出。
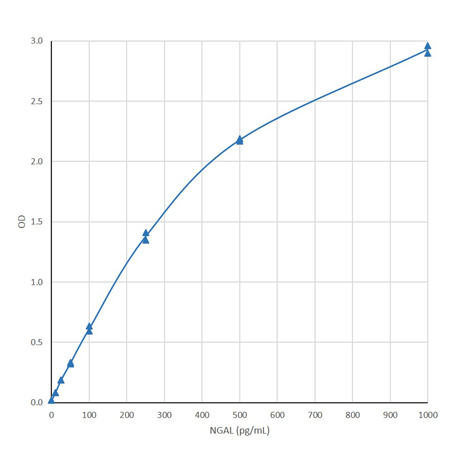
NGAL(人)ELISA 试剂盒,可在 450 nm 处高灵敏度检测人样本中 NGAL,低至 4 pg/mL。
◆特点
● 96 孔板检测,只需 4 小时即可快速检测最多 40 个样品及其平行组
● 高灵敏检测,可检测低至 4 pg/mL 的 NGAL
● 试剂盒包含即用型预涂板和独立标准溶液,可节省时间并减少操作失误
● 全定量分析,有别于半定量分析的免疫印迹法
◆NGAL(人)ELISA试剂盒(KIT 036)- 标准曲线
◆产品详情
NGAL别称 | 中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白、脂质运载蛋白2、铁运载蛋白、癌基因产物24p3 |
灵敏度 | 4 pg/mL(范围10-1000 pg/mL) |
检测时间 | 小于4小时 |
应用 | ELISA、比色检测 |
应用说明 | 用于定量检测人尿液、血浆、血清、组织提取物和培养上清液中的NGAL |
波长 | 450 nm |
物种反应性 | 人 |
运输条件 | 非冷冻蓝冰 |
长期储存 | +4°C |
组分 | 1. 12 × 8 孔微孔板条,每条均涂有抗 NGAL抗体(共96孔)+板条框 2. 样品稀释液 3. NGAL标准溶液1-8:0,10,25,50,100,250,500,1000 pg/mL 4. 25X浓缩洗涤液 5. 生物素化 NGAL 抗体 6. HRP-链霉亲和素偶联物 7. TMB底物 8. 终止液 |
技术信息/产品说明 | 点击此处查看操作手册 |
UniProt ID | P80188 |
监管状态 | RUO – 仅供研究用 |
制造商 | BioPorto Diagnostics |
◆产品列表
产品编号 | 产品名称 | 包装 |
NGAL (human) ELISA kit | 96 wells |
◆其他物种的 NGAL 试剂盒
除NGAL (人) ELISA试剂盒外,另可提供小鼠、大鼠、猪、狗、猴的 NGAL ELISA 试剂盒。
产品编号 | 产品名称 | 包装 |
NGAL (mouse) ELISA kit | 96 wells | |
NGAL (dog) ELISA kit | 96 wells | |
NGAL (pig) ELISA kit | 96 wells | |
NGAL (monkey) ELISA kit | 96 wells | |
NGAL (rat) ELISA kit | 96 wells |
参考文献
1. | The Effects of Beverage Intake after Exhaustive Exercise on Organ Damage, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Healthy Males: T. Tominaga, et al.; Antioxidants (Basel) 10, 866 (2021), Application(s): NGAL quantification on human urine samples, 摘要; 全文 |
2. | Prognostic value of urinary calprotectin, NGAL and KIM-1 in chronic kidney disease: F.S. Seibert, et al.; Kidney Blood Press. Res. 43, 1255 (2018), Application(s): ELISA using human urine, 摘要; |
3. | Acute kidney injury prediction in cardiac surgery patients by a urinary peptide pattern: a case-control validation study: J. Metzger, et al.; Crit. Care 20, 157 (2016), 摘要; 全文 |
4. | An AKI biomarker lipocalin 2 in the blood derives from the kidney in renal injury but from neutrophils in normal and infected conditions: J. Kanda, et al.; Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 19, 99 (2015), 摘要; |
5. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts kidney outcome and death in patients with cirrhosis and bacterial infections: R. Barreto, et al.; J. Hepatol. 61, 35 (2014), Application(s): ELISA using human urine, 摘要; |
6. | A comparison of the analytical performance of five commercially available assays for neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin using urine: R.L. Kift, et al.; Ann. Clin. Biochem. 50, 236 (2013), 摘要; |
7. | Albumin oxidation leads to neutrophil activation in vitro and inaccurate measurement of serum albumin in patients with diabetic nephropathy: R. Michelis, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 60, 49 (2013), 摘要; |
8. | Association between plasma neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin level and obstructive sleep apnea or nocturnal intermittent hypoxia: K. Murase, et al.; PLoS One 8, e54184 (2013), 摘要; |
9. | BK virus-associated nephropathy: neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a new diagnostic tool?: S. Rau, et al.; Clin. Transplant. 27, E184 (2013), 摘要; |
10. | Can neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin help depict early contrast material-induced nephropathy?: A. Lacquaniti, et al.; Radiology 267, 86 (2013), 摘要; |
11. | Circulating levels of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) correlate with the presence and severity of preeclampsia: S.M. Kim, et al.; Reprod. Sci. 20, 1083 (2013), 摘要; |
12. | Day-to-day variation of urinary NGAL and rational for creatinine correction: J. Helmersson-Karlqvist, et al.; Clin. Biochem. 46, 70 (2013), 摘要; |
13. | Differential expression of cancer-associated proteins in breastmilk: W. Qin, et al.; Breastfeed Med. 8, 120 (2013), 摘要; |
14. | Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury: K. Kashani, et al.; Crit. Care 17, R25 (2013), 摘要; |
15. | Impact of severe sepsis on serum and urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: an observational study: M. Di Nardo, et al.; Blood Purif. 35, 172 (2013), 摘要; |
16. | Prognostic value of serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in metastatic and nonmetastatic colorectal cancer: J. Martí, et al.; World J. Surg. 37, 1103 (2013), 摘要; |
17. | Prophylactic perioperative sodium bicarbonate to prevent acute kidney injury following open heart surgery: a multicenter double-blinded randomized controlled trial: M. Haase, et al.; PLoS Med. 10, e1001426 (2013), 摘要; |
18. | Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a predictor of the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants: H. Inoue, et al.; Early Hum. Dev. 89, 425 (2013), 摘要; |
19. | The clinical utility of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in acute kidney injury: J.W. Pickering, et al.; Blood Purif. 35, 295 (2013), 摘要; |
20. | The role of urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in critically ill patients: E. Cho, et al.; J. Korean Med. Sci. 28, 100 (2013), 摘要; |
21. | Urine Biomarkers Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1) Have Different Patterns in Heart Failure Exacerbation: M. Park, et al.; Biomark. Insights 8, 15 (2013), 摘要; |
22. | Albuminuria increases cystatin C excretion: implications for urinary biomarkers: M. Nejat, et al.; Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 27 Suppl 3, iii96 (2012), 摘要; |
23. | Are serum and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predictive of renal graft function in short term?: N. Rahimzadeh, et al.; Pediatr. Transplant. 16, 796 (2012), 摘要; |
24. | Association between systemic neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and anemia, relative hypochromia, and inflammation in chronic systolic heart failure: K. Shrestha, et al.; Congest. Heart Fail. 18, 239 (2012), 摘要; |
25. | Delayed graft function (DGF) after living donor kidney transplantation: a study of possible explanatory factors: J. Salamzadeh, et al.; Ann. Transplant. 17, 69 (2012), 摘要; |
26. | Evaluation of the impact of shock wave lithotripsy on kidneys using a new marker: how do neutrophil gelatinese-associated lypocalin values change after shock wave lithotripsy?: F. Zekey, et al.; Urology 80, 267 (2012), 摘要; |
27. | Failure of remote ischemic preconditioning to reduce the risk of postoperative acute kidney injury in children undergoing operation for complex congenital heart disease: a randomized single-center study: K.R. Pedersen, et al.; J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 143, 576 (2012), 摘要; |
28. | Failure of remote ischemic preconditioning to reduce the risk of postoperative acute kidney injury in children undergoing operation for complex congenital heart disease: a randomized single-center study: K.R. Pedersen, et al.; J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 143, 576 (2012), 摘要; |
29. | Mild elevation of urinary biomarkers in prerenal acute kidney injury: K. Doi, et al.; Kidney Int. 82, 1114 (2012), 摘要; |
30. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an early biomarker of acute kidney injury in liver transplantation: T.D. Jeong, et al.; Clin. Transplant. 26, 775 (2012), 摘要; |
31. | Renal function and solitary kidney disease: Wilms tumour survivors versus patients with unilateral renal agenesis: J. Stefanowicz, et al.; Kidney Blood Press. Res. 35, 174 (2012), 摘要; |
32. | Serum levels of gelatinase associated lipocalin as indicator of the inflammatory status in coronary artery disease: N. Kafkas, et al.; Int. J. Inflam. 2012, 189797 (2012), 摘要; |
33. | Spironolactone diminishes urinary albumin excretion in patients with type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a randomized placebo-controlled crossover study: S.E. Nielsen, et al.; Diabet. Med. 29, e184 (2012), 摘要; |
34. | The effect of RAAS blockade on markers of renal tubular damage in diabetic nephropathy: u-NGAL, u-KIM1 and u-LFABP: S.E. Nielsen, et al.; Scand J. Clin. Lab Invest. 72, 137 (2012), 摘要; |
35. | Urinary markers of kidney injury and kidney function decline in HIV-infected women: M.G. Shlipak, et al.; J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 61, 565 (2012), 摘要; |
36. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin accurately detects acute allograft rejection among other causes of acute kidney injury in renal allograft recipients: N. Heyne, et al.; Transplantation 93, 1252 (2012), 摘要; |
37. | Urinary NT-proBNP, NGAL, and H-FABP may predict hemodynamic relevance of patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants: V. Tosse, et al.; Neonatology 101, 260 (2012), 摘要; |
38. | Clinical outcome of renal tubular damage in chronic heart failure: K. Damman, et al.; Eur. Heart J. 32, 2705 (2011), 摘要; |
39. | Improved performance of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in the critically ill by stratification for injury duration and baseline renal function: Z.H. Endre, et al.; Kidney Int. 79, 1119 (2011), 摘要; |
40. | Kidney injury molecule-1 and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase in chronic heart failure: possible biomarkers of cardiorenal syndrome: C.G. Jungbauer, et al.; Eur. J. Heart. Fail. 13, 1104 (2011), 摘要; |
41. | KIM-1 and NGAL: new markers of obstructive nephropathy: A. Wasilewska, et al.; Pediatr. Nephrol. 26, 579 (2011), 摘要; |
42. | Molecular MRI of murine atherosclerotic plaque targeting NGAL: a protein associated with unstable human plaque characteristics: B.C. te Boekhorst, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 89, 680 (2011), 摘要; |
43. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin at ICU admission predicts for acute kidney injury in adult patients: H.R. H. de Geus, et al.; Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 183, 907 (2011), 摘要; |
44. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass: C.D. Krawczeski, et al.; J. Pediatr. 158, 1009 (2011), 摘要; |
45. | Renal dysfunction is a stronger determinant of systemic neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels than myocardial dysfunction in systolic heart failure: K. Shrestha, et al.; J. Card. Fail. 17, 472 (2011), 摘要; |
46. | Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin - a sensitive novel marker of renal impairment in liver cirrhosis?: A.L. Gerbes, et al.; Digestion 84, 82 (2011), 摘要; |
47. | Temporal relationship and predictive value of urinary acute kidney injury biomarkers after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass: C.D. Krawczeski, et al.; J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58, 2301 (2011), 摘要; |
48. | Tubular markers do not predict the decline in glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy: S.E. Nielsen, et al.; Kidney Int. 79, 1113 (2011), 摘要; |
49. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients in a four-year follow-up study: S.E. Nielsen, et al.; Nephron Clin. Pract. 118, c130 (2011), 摘要; |
50. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of acute kidney injury after orthotopic liver transplantation: G. Wagener, et al.; Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 26, 1717 (2011), 摘要; |
51. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin at birth predicts early renal function in very low birth weight infants: G. La Manna, et al.; Pediatr. Res. 70, 379 (2011), 摘要; |
52. | Volume status and diuretic therapy in systolic heart failure and the detection of early abnormalities in renal and tubular function: K. Damman, et al.; J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 57, 2233 (2011), 摘要; |
53. | Bile duct ligation in developing rats: temporal progression of liver, kidney, and brain damage: J.M. Sheen, et al.; J. Pediatr. Surg. 45, 1650 (2010), 摘要; |
54. | Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM1) in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a cross-sectional study and the effects of lisinopril: S.E. Nielsen, et al.; Diabet. Med. 27, 1144 (2010), 摘要; |
55. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): validation of commercially available ELISA: K.R. Pedersen, et al.; Scand J. Clin. Lab Invest. 70, 374 (2010), 摘要; |
56. | Pathological significance of a panel of urinary biomarkers in patients with drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis: Y. Wu, et al.; Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 5, 1954 (2010), 摘要; |
57. | Possible relationship between neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, hepcidin, and inflammation in haemodialysed patients: J. Malyszko, et al.; Nephron Clin. Pract. 115, c268 (2010), 摘要; |
58. | Safety of low volume iodinated contrast administration for arteriovenous fistula intervention in chronic kidney disease stage 4 or 5 utilizing a bicarbonate prophylaxis strategy: E. Eisenhart, et al.; Semin. Dial. 23, 638 (2010), 摘要; |
59. | Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin correlates with kidney function in heart allograft recipients: P. Przybylowski, et al.; Transplant Proc. 42, 1797 (2010), 摘要; |
60. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel biomarker for disease activity in lupus nephritis: T. Rubinstein, et al.; Rheumatology (Oxford) 49, 960 (2010), 摘要; |
61. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: A potential biomarker for predicting rapid progression of drug-induced chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis: Y. Wu, et al.; Am. J. Med. Sci. 339, 537 (2010), 摘要; |
62. | Urinary neutrophil-gelatinase associated lipocalin is a potential noninvasive marker for renal scarring in patients with vesicoureteral reflux: M. Ichino, et al.; J. Urol. 183, 2001 (2010), 摘要; |
63. | Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: an independent predictor of adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury: H.N. Yang, et al.; Am. J. Nephrol. 31, 501 (2010), 摘要; |
64. | Implication of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor induced neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis revealed by proteome analysis: M. Katano, et al.; Arthritis Res. Ther. 11, R3 (2009), 摘要; |
65. | NGAL: a new missing link between inflammation and uremic anemia?: D. Bolignano, et al.; Ren. Fail. 31, 622 (2009), 摘要; |
66. | Comparison of the effects of gelatin and a modern hydroxyethyl starch solution on renal function and inflammatory response in elderly cardiac surgery patients: J. Boldt, et al.; Br. J. Anaesth. 100, 457 (2008), 摘要; |
67. | Effect of a single intravenous immunoglobulin infusion on neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels in proteinuric patients with normal renal function: D. Bolignano, et al.; J. Investig. Med. 56, 997 (2008), 摘要; |
68. | Increased incidence of acute kidney injury with aprotinin use during cardiac surgery detected with urinary NGAL: G. Wagener, et al.; Am. J. Nephrol. 28, 576 (2008), 摘要; |
69. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of disease activity in pediatric lupus nephritis: M. Suzuki, et al.; Pediatr. Nephrol. 23, 403 (2008), 摘要; |
70. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expression in chronic myeloid leukemia: C. Villalva, et al.; Leuk. Lymphoma 49, 984 (2008), 摘要; |
71. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin reflects the severity of renal impairment in subjects affected by chronic kidney disease: D. Bolignano, et al.; Kidney Blood Press. Res. 31, 255 (2008), 摘要; |
72. | NGAL (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) and cystatin C: are they good predictors of contrast nephropathy after percutaneous coronary interventions in patients with stable angina and normal serum creatinine?: H. Bachorzewska-Gajewska, et al.; Int. J. Cardiol. 127, 290 (2008), 摘要; |
73. | NGAL (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) and cystatin C: are they good predictors of contrast nephropathy after percutaneous coronary interventions in patients with stable angina and normal serum creatinine?: H. Bachorzewska-Gajewska, et al.; Int. J. Cardiol. 127, 290 (2008), 摘要; |
74. | Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of renal function in non-diabetic patients with stage 2-4 chronic kidney disease: J. Malyszko, et al.; Ren. Fail. 30, 625 (2008), 摘要; |
75. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL), a marker of tubular damage, is increased in patients with chronic heart failure: K. Damman, et al.; Eur. J. Heart Fail. 10, 997 (2008), 摘要; |
76. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is associated with severity of renal disease in proteinuric patients: D. Bolignano, et al.; Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 23, 414 (2008), 摘要; |
77. | Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: G. Wagener, et al.; Am. J. Kidney Dis. 52, 425 (2008), 摘要; |
78. | Urinary NGAL in premature infants: A.P. Lavery, et al.; Pediatr. Res. 64, 423 (2008), 摘要; |
79. | Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-18 predict acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: C. Xin, et al.; Ren. Fail. 30, 904 (2008), 摘要; |
80. | Urine NGAL predicts severity of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a prospective study: M. Bennett, et al.; Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 3, 665 (2008), 摘要; |
81. | Could neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin and cystatin C predict the development of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary interventions in patients with stable angina and normal serum creatinine values?: H. Bachorzewska-Gajewska, et al.; Kidney Blood Press. Res. 30, 408 (2007), 摘要; |
82. | Detection of subclinical tubular injury after renal transplantation: comparison of urine protein analysis with allograft histopathology: S. Schaub, et al.; Transplantation 84, 104 (2007), 摘要; |
83. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) correlations with cystatin C, serum creatinine and eGFR in patients with normal serum creatinine undergoing coronary angiography: H. Bachorzewska-Gajewska, et al.; Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 22, 295 (2007), 摘要; |
84. | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease: D. Bolignano, et al.; Am. J. Nephrol. 27, 373 (2007), 摘要; |
85. | Neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin and renal function after percutaneous coronary interventions: H. Bachorzewska-Gajewska, et al.; Am. J. Nephrol. 26, 287 (2006), 摘要; |
其他参考文献
1. | Application of emerging biomarkers of acute kidney injury in development of kidney-sparing polypeptide-based antibiotics: D. Burt, et al.; Drug Chem. Toxicol. 37, 204 (2014), 摘要; |
| 免责声明 |
|
1. 本公司密切关注本网站发布的内容,但不保证发布内容的准确性、完整性、可靠性和最新性等。 2. 本公司不保证使用本网站期间不会出现故障或计算机病毒污染的风险。 3. 无论何种原因,使用本网站时给用户或第三方造成的任何不利或损害,本公司概不负责。此外,对于用户与其他用户或第三方之间因本网站发生的任何交易、通讯 3. 或纠纷,本公司概不负责。 4. 本网站可提供的所有产品和服务均不得用于人体或动物的临床诊断或治疗,仅可用于科研等非医疗目的。如任何用户将本网站提供的产品和服务用于临床诊断或治 4. 疗,以及其他特定的用途或行为,本公司概不保证其安全性和有效性,并且不负任何相关的法律责任。 |