炎性体是介导caspase-1活化的多蛋白复合物, 它可以促进除了别的以外的促炎细胞因子白介素(IL)-1β和 IL-18的分泌物。nod样受体家族的 NLRP3/NALP3是发危险信号到caspase-1活化炎性体的关键组成部分。NLRP3缺陷是导致家族性寒冷型自身炎症综合征1型(FCAS1)、Muckle-Wells 综合征 (MWS) 和慢性炎症性神经,皮肤,关节综合征的原因。
产品数据 | ||
产品别名 | NACHT-, LRR- and PYD-containing Protein 3; NLRP3; Cryopyrin; | |
抗小鼠NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-1) | NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-2) | |
特性 | ||
集落 | Cryo-1 | Cryo-2 |
同型 | 小鼠IgG2b | |
来源/宿主 | 纯化浓缩的杂交瘤细胞组织培养上清液。 | |
应用 | Western印迹:(1 μg/mL) | Western印迹:(1 μg/mL) 免疫细胞化学:1. see J. Virol. 85, 13019 (2011) 2. Nat. Immunol. 13, 255 (2012) 免疫沉淀:in RIPA buffer, see Mol. Cell 49, 331(2012) 免疫组化:1:200, for a protocol see Nature 493, 67 (2012) ChIP assay:2 µg/DNA of 10E6 cells (see Nat. Immunol. 16, 859 (2015)) |
交叉反应性 | 小鼠 | 人,小鼠 |
特异性 | 识别小鼠NLRP3/ NALP3 | 识别人,小鼠的NLRP3/ NALP3 |
纯度 | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) | |
浓度详情 | Protein G-affinity purified. | |
浓度 | 1 mg/mL | |
配方 | 液体、含10%甘油的PBS和0.02%的叠氮化钠。 | |
产品类型 | 单克隆抗体 | |
运输和装卸 | ||
运输 | BLUE ICE | |
短期储存温度 | +4°C | |
长期储存温度 | -20°C | |
建议处置方式 | 开封后, 分装并储存在-20°C的地方,避免冷冻/解冻循环。 | |
使用/稳定性 | 收货后保存在-20°C的地方,可稳定保存至少一年。 | |
抗小鼠NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-1)
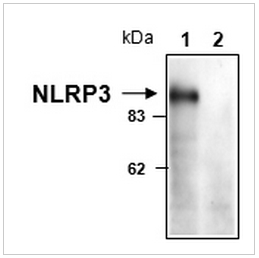
使用抗小鼠NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-1)检测小鼠巨噬细胞中NLRP3的含量。
细胞提取物来源于小鼠巨噬细胞WT(泳道1)或NLRP3 KO(泳道2), 在还原条件下用SDS-PAGE 分离, 转移到硝酸纤维素膜后,用抗小鼠NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-1) (1 μg/mL) 孵育并检测。在化学发光检测系统中,蛋白质是可视化的。
NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-2)
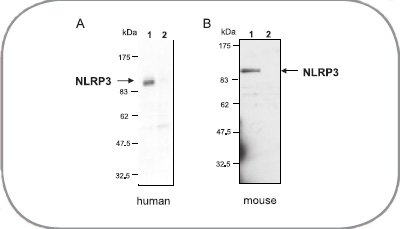
用anti-NLRP3/NALP3, mAb (Cryo-2)分别检测人和小鼠的THP1 细胞及巨噬细胞中的NLRP3/NALP3 含量。
A)细胞提取物来自于人THP1 细胞(泳道1)或THP1 表达的shRNA hNLRP3(泳道2)
B)细胞提取物来自于小鼠巨噬细胞 WT(泳道1)或NLRP3/NALP3 KO(泳道2),用SDS-PAGE 电泳分离,转移到硝酸纤维素膜后,
用anti-NLRP3/NALP3,mAb (Cryo-2) (1 μg/mL) 孵育,并检测。在化学发光检测系统中,蛋白质是可视化的。

使用NLRP3(Cryo-2)单抗(产品编号AG-20B-0014)在小鼠巨噬细胞中检测小鼠NLRP3。
实验方法:从小鼠巨噬细胞(BMDM)WT +/+(lane 1),NLRP3 +/-(lane 2)或NLRP3 -/- (lane 3)的细胞提取物,有或没
有用LPS(50n g/mL)处理3 h,在还原条件下通过SDS-PAGE分离,转移至硝酸纤维素膜并与NLRP3(Cryo-2)的
mAb(1 μg/mL)共同孵育。 蛋白通过化学发光显影。图片由德国慕尼黑大学的Dr. Olaf Gross提供。
产品编号 | 产品名称 | 规格 |
AG-20B-0006-C100 | anti-NLRP3/NALP3 (mouse), mAb (Cryo-1) | 100 μg |
AG-20B-0014-C100 | anti-NLRP3/NALP3, mAb (Cryo-2) | 100 μg |
欲了解更多产品相关资讯,请点击文字:
1. | Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation: R. Zhou, et al.; Nature Immunology 11, 136 (2010) |
2. | The NLRP3 inflammasome promotes renal inflammation and contributes to CKD: A. Vilaysane, et al.; J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 21, 1732 (2010) |
3. | A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation: R. Zhou, et al.; Nature 469, 221 (2011) |
4. | Differential expression of NLRP3 among hematopoietic cells: G. Guarda, et al.; J. Immunol. 186, 2529 (2011) |
5. | Mechanism of Impaired NLRP3 Inflammasome Priming by Monophosphoryl Lipid A: C.A. Embry, et al.; Sci. Signal. 4, ra28 (2011) |
6. | Measles Virus V Protein Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Interleukin-1 Secretion: N. Komune, et al.; J. Virol. 85, 13019 (2011) |
7. | Novel role of PKR in inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release: B. Lu, et al.; Nature 488, 670 (2012) |
8. | Deubiquitination of NLRP3 by BRCC3 Critically Regulates Inflammasome Activity: B.F. Py, et al.; Mol. Cell 49,331 (2012) |
9. | NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer's disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice: M.T. Heneka, et al.; Nature 493, 67 (2012) |
10. | Activation of autophagy by inflammatory signals limits IL-1b production by targeting ubiquitinated inflammasomes for destruction: C.-S. Shi, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 13, 255 (2012) |
11. | Inflammasome-independent NLRP3 augments TGF-β signaling in kidney epithelium: W. Wang, et al.; J. Immunol. 190, 1239 (2013) |
12. | Omega-3 Fatty Acids Prevent Inflammation and Metabolic Disorder through Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Y. Yan, et al.; Immunity 38, 1154 (2013) |
13. | LRRFIP2 negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages by promoting Flightless-I-mediated caspase-1 inhibition: J. Jin, et al.; Nat. Commun. 4, 2075 (2013) |
14. | Proapoptotic Chemotherapeutic Drugs Induce Noncanonical Processing and Release of IL-1β via Caspase-8 in Dendritic Cells: C. Antonopoulus, et al. J. Immunol. 191, 4789 (2013) |
15. | Constitutively activated NLRP3 inflammasome causes inflammation and abnormal skeletal development in mice: S.L. Bonar, et al.; PLoS One 7, e35979 (2012) |
16. | FADD and caspase-8 mediate priming and activation of the canonical and noncanonical Nlrp3 inflammasomes: P. Gurung, et al.; J. Immunol. 192, 1835 (2014) |
17. | XIAP Restricts TNF- and RIP3-Dependent Cell Death and Inflammasome Activation: M. Yabal, et al.; Cell Rep.7, 1796 (2014) |
18. | The adaptor ASC has extracellular and 'prionoid' activities that propagate inflammation: B.S. Franklin, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 15, 727 (2014) |
19. | The NLRP3 inflammasome is released as a particulate danger signal that amplifies the inflammatory response: A. Baroja-Mazo, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 15, 738 (2014) |
20. | Toward a chemical marker for inflammatory disease: a fluorescent probe for membrane-localized thioredoxin: M.H. Lee, et al.; JACS 136, 8430 (2014) |
21. | Prostaglandin E2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through EP4 receptor and intracellular cyclic AMP in human macrophages: M. Sokolowska, et al.; J. Immunol. 194, 5472 (2015) |
22. | The receptor NLRP3 is a transcriptional regulator of TH2 differentiation: M. Bruchard, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 16,859 (2015) |
23. | NLRP3 Inflammasome Is Expressed and Functional in Mouse Brain Microglia but Not in Astrocytes: A. Gustin, et al.; PLos One 10, e0130624 (2015) |
24. | Nlrp6 promotes recovery after peripheral nerve injury independently of inflammasomes: E. Ydens, et al.; J. Neuroinfl. 12, 143 (2015) |
25. | The Crohn’s disease risk factor IRGM limits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by impeding its assembly and by mediating its selective autophagy: S. Mehto, et al.; Mol. Cell 73, 429 (2019) |
26. | Lack of Protein Prenylation Promotes Nlrp3 Inflammasome Assembly in Human Monocytes: O.P. Skinner, et al.; J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. (Epub ahead of print) (2019) |
| 产品编号 | 产品名称 | 产品规格 | 产品等级 | 备注 |
| AG-20B-0006-C100 | anti-NLRP3/NALP3 (mouse), mAb (Cryo-1) 抗小鼠NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-1) |
100 μg | - | - |
| AG-20B-0014-C100 | anti-NLRP3/NALP3, mAb (Cryo-2) NLRP3/NALP3单抗(Cryo-2) |
100 μg | - | - |
| 免责声明 |
|
1. 本公司密切关注本网站发布的内容,但不保证发布内容的准确性、完整性、可靠性和最新性等。 2. 本公司不保证使用本网站期间不会出现故障或计算机病毒污染的风险。 3. 无论何种原因,使用本网站时给用户或第三方造成的任何不利或损害,本公司概不负责。此外,对于用户与其他用户或第三方之间因本网站发生的任何交易、通讯 3. 或纠纷,本公司概不负责。 4. 本网站可提供的所有产品和服务均不得用于人体或动物的临床诊断或治疗,仅可用于科研等非医疗目的。如任何用户将本网站提供的产品和服务用于临床诊断或治 4. 疗,以及其他特定的用途或行为,本公司概不保证其安全性和有效性,并且不负任何相关的法律责任。 |